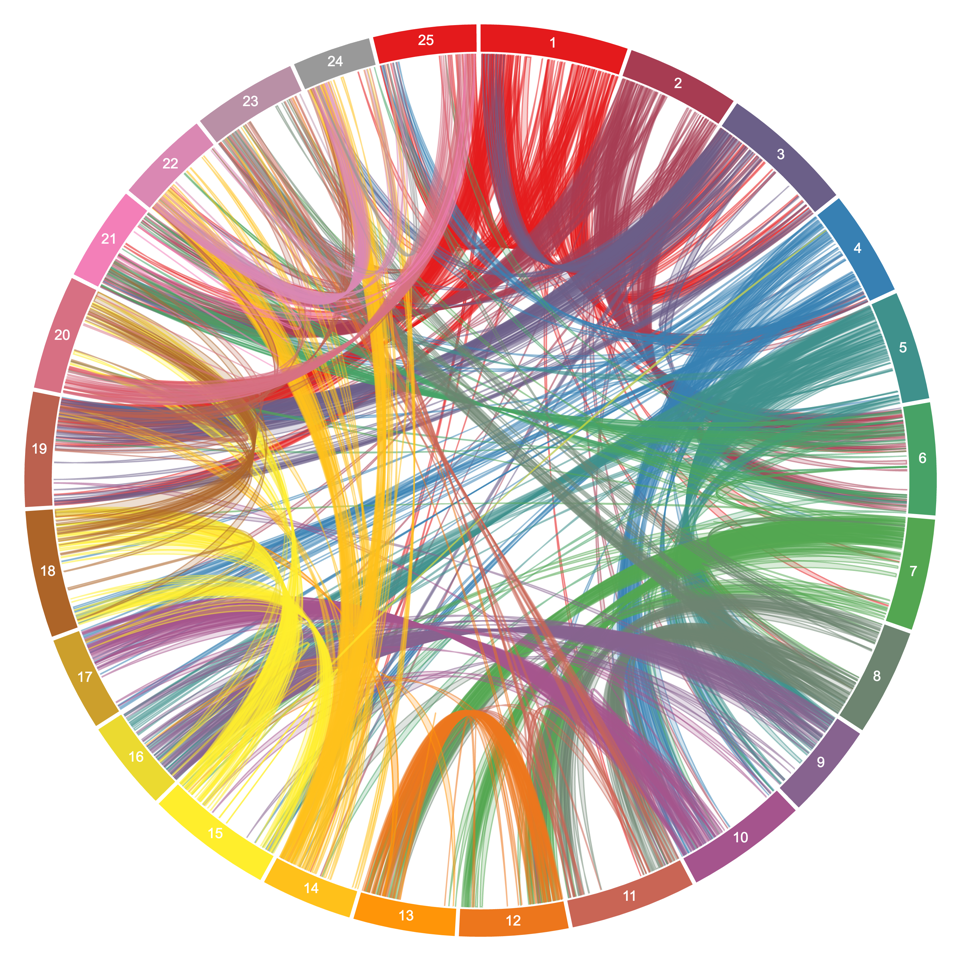
White Lupin Genome
By Peret Lab

High quality white lupin genome sequence
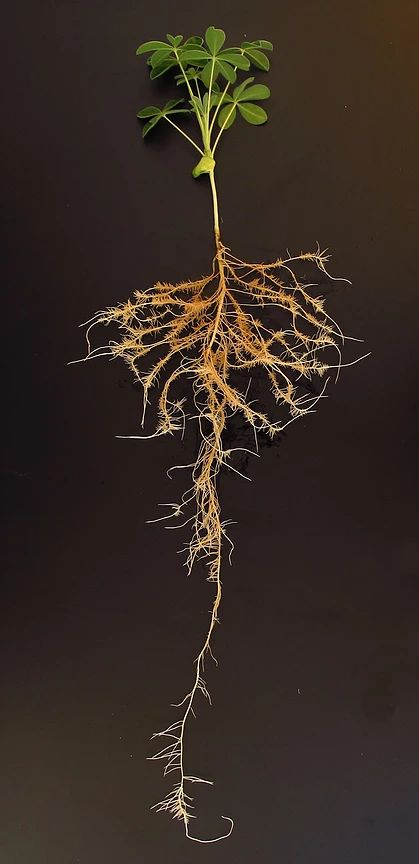
We generated a high quality assembly of the white lupin (Lupinus albus) genome sequence from the cultivated AMIGA variety. Plant DNA was sequenced using long reads (PacBio), optical maps (BioNano Genomics) and short reads (Illumina). We integrated genetic maps (from Książkiewicz et al., 2017) to further improve the assembly. This website gathers all genomic resources and information related to this project. We made an effort to make all raw data available here and on public repositories.
Browse the white lupin genome
This website integrates a Genome Browser that combines the reference genome as well as 15 resequenced white lupin varieties. Here is the detail of the available tracks :
- Annotations: gene annotation based on gene prediction and transcriptomics data (see 10 organs below)
- Spatial RNA-seq: Transcriptomics dataset from cluster roots that were sectioned into 8 developmental parts
- Secco RNA-seq: reassembly of the previously published cluster root dataset from Secco et al., 2014
- 10 organs: Transcriptomics dataset from 10 white lupin organs used for annotation purposes
- 15 varieties: Resequencing of the following varieties (Amiga, Clovis, Dieta, Energy, Feodora, Figaro, GR38, Kiev, Graecus, Lucky, Luxe, Magnus, Orus, P27174 and Ulysse).
White lupin sequences
Using the Sequences tab, you can access various sequences from gene ID, BLAST or keyword search.
- Get specific gene sequence : allows you to quickly access CDS, mRNA, protein and even 2kb promoter sequence from a list of white lupin genes
- BLAST against lupin genome : allows you to BLAST any sequence against the white lupin genome
- Keyword search : allows you to search genes by keywords
- Find similar genes : allows you to quickly identify orthologous genes from a list of white lupin genes
Cluster root transcriptomic data
Using the Expression tab, you can access several tools to dive into gene expression along cluster root formation.
- Gene expression profile : allows you to enter a list of white lupin genes and directly access their expression profile in cluster root (spatial RNAseq)
- miRNA expression profile : allows you to enter a list of white lupin miRNA and directly access their expression profile in cluster root (spatial RNAseq)
Download
You can access all raw genomic and transcriptomic data from the white lupin genome project. Please report any dead links.
Consortium
The white lupin genome project is the result of a collaborative work coordinated by the Peret Lab and funded as part of the ERC LUPIN ROOT project. This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 637420). You can find the contributions of the project partners under the Consortium tab
Project leader
The Peret lab is interested in root development and has established white lupin as a model because it produces cluster roots (CRs) as an adaptation to low phosphorus. These structures can mobilize and acquire phosphate very efficiently and white lupin is known as a crop with low needs for phosphate fertilizer input. The massive production of lateral organs is a great opportunity for developmental studies and we are interested in various aspects of white lupin CRs development such as the control of CRs initiation and the programmed rootlet determinacy. More info here.
Bioinformatics tools
Here is a list of the main tools that were used on this portal :
- Jbrowse : Buels R et al. JBrowse: a dynamic web platform for genome visualization and analysis.Genome Biology (2016) (link)
- SequenceServer : Priyam A, Woodcroft BJ, Rai V, Munagala A, Moghul I, Ter F, Gibbins MA, Moon H, Leonard G, Rumpf W & Wurm Y. 2015. Sequenceserver: a modern graphical user interface for custom BLAST databases. biorxiv doi: 10.1101/033142. (link)
- DESeq2 : Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014). “Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2.” Genome Biology, 15, 550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 (link)
- ShortStack : Johnson NR, Yeoh JM, Coruh C, Axtell MJ. (2016). G3 6:2103-2111. doi:10.1534/g3.116.030452 (link)
Citation
Bárbara Hufnagel, André Marques, Alexandre Soriano, Laurence Marquès, Fanchon Divol, Patrick Doumas, Erika Sallet, Davide Mancinotti, Sébastien Carrere, William Marande, Sandrine Arribat, Jean Keller, Cécile Huneau, Thomas Blein, Delphine Aime, Malika Laguerre, Jemma Taylor, Veit Schubert, Matthew Nelson, Fernando Geu-Flores, Martin Crespi, Karine Gallardo-Guerrero, Pierre-Marc Delaux, Jérôme Salse, Hélène Bergès, Romain Guyot, Jérôme Gouzy, Benjamin Péret
Nature communication 2020 : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-14197-9
Plasticity team on Twitter
Tweets by PeretLab